基础操作
起别名
select 别名.字段1,别名.字段2,... from 表名 as 别名
select 字段1 as 别名1,字段2 as 别名2,... from 表名
例:select s.name,s.sex,s.age from students as s;
例:select name as 姓名,sex as 性别,age as 年龄 from students;去重
select distinct 字段1,... from 表名
例:select distinct sex from students;一、条件查询
语言格式
select 字段1,字段2... from 表名 where 条件;
例: select * from students where id=1;BINARY 关键字:1.来设定 WHERE 子句的字符串比较是区分大小写的。2.字段中有中文字符时,需要使用BINARY关键字,否则查询出来的字段会是乱码
比较运算
| > | < | >= | <= | = | !=或<> |
例1:查询小乔的年龄
select age from students where name='小乔’
例2:查询20岁以下的学生
select * from students where age<20
例3:查询家乡不在北京的学生
select * from传智教育-黑马程序员 students where hometown!='北京'逻辑运算
| and | or | not |
例1:查询年龄小于20的女同学
select * from students where age<20 and sex='女'
例2:查询女学生或'1班'的学生
select * from students where sex='女' or class='1班
例3:查询非天津的学生
select * from students where not hometown='天津'模糊查询
| 关键字 | 匹配任意多个字符 | 匹配一个任意字符 |
| like | % | – |
例1:查询姓孙的学生
select * from students where name like '孙%'
例2:查询姓孙且名字是一个字的学生
select * from students where name like '孙_'范围查询
| 非连续范围 | 连续范围 |
| in() | between….and…. |
例1:查询家乡是北京或上海或广东的学生
select * from students where hometown in('北京','上海','广东')
例2:查询年龄为18至20的学生
select * from students where age between 18 and 20空判断
注意:Mysql中空表示null,与 ‘’ (空)是不一样的。
| 判断为空 | 判断不为空 |
| is null | is not null |
例1:查询没有填写身份证的学生
select * from students where card is null
例2:查询填写了身份证的学生
select * from students where card is not null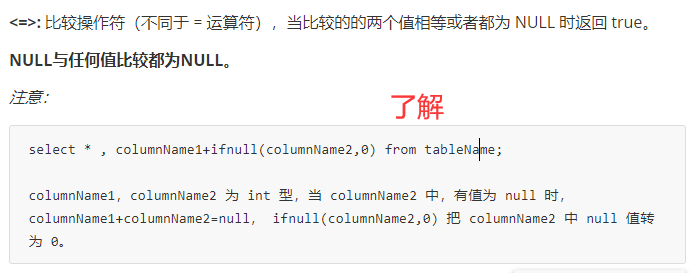
二、排序
Order by:结果排序后再返回结果
select * from 表名 order by 字段名1 asc|desc, 字段名2 asc|desc,...desc : descending order 降序
asc : ascending order 升序 (默认)
三、聚合函数
| max() | min() | sum() | avg() | count() |
例1:查询学生总数
select count(*) from students;
例2:查询女生的最大年龄
select max(age) from students where sex='女';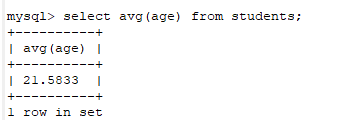
四、分组查询
Group by:按照字段分组,此字段相同的数据会被放到一个组中
分组的目的:是对每一组的数据进行统计(使用聚合函数)
select 字段1,字段2,聚合函数... from 表名 group by 字段1,字段2...
例1:查询各种性别的人数
select sex,count(*) from students group by sex
例2:查询每个班级中各种性别的人数
select class,sex,count(*) from students group by class,sex
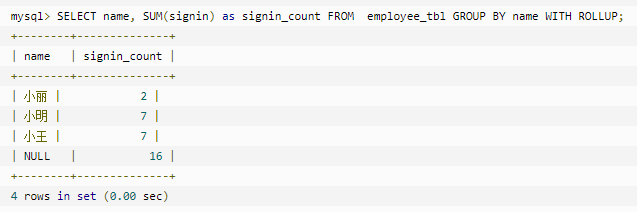
1.WITH ROLLUP
可以实现在分组统计数据基础上再进行相同的统计(SUM,AVG,COUNT…)。
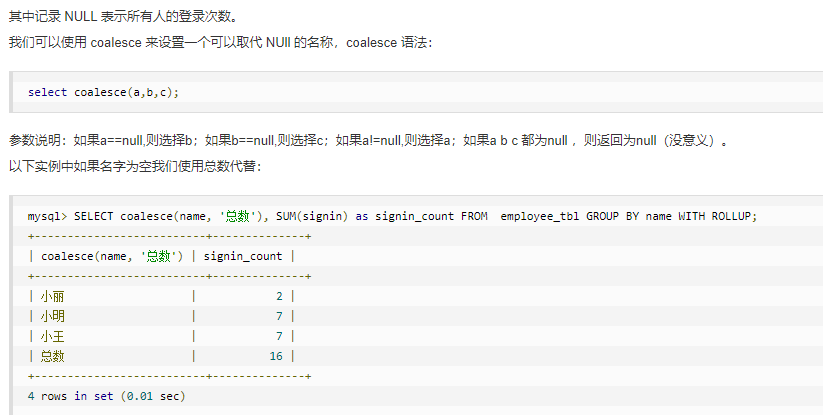
2.分组后的数据筛选
说明: 关键字having后面的条件运算符与where的相同
select 字段1,字段2,聚合... from 表名 group by 字段1,字段2,字段3...having 条件区别如下:
1.where 是对 from 后面指定的表进行数据筛选, 属于对原始数据的筛选。
2.having 是对 group by 的结果进行筛选。
3.having 后面的条件中可以用聚合函数,where 后面不可以。
例1:查询男生总人数
方案一:select count(*) from students where sex='男'
方案二:select sex,count(*) from students group by sex having sex='男'五、分页查询
1.获取部分数据
select * from 表名 limit start,count说明:从start开始,获取count条数据。start索引从0开始
2.分页实现
select * from students limit (n-1)*m, m说明:n表示显示第几页的数据 ,m表示每页显示多少条数据
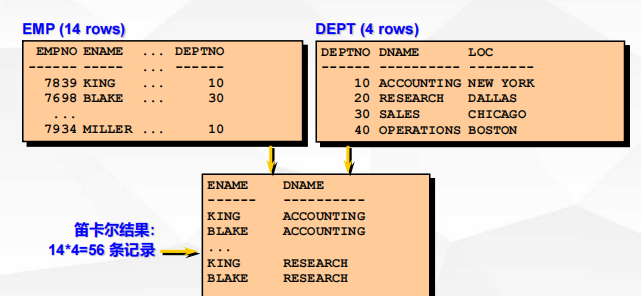
六、连接查询
SELECT, UPDATE 和 DELETE 语句中使用 Mysql 的 JOIN 来联合多表查询。
内连接
inner join(join): 连接两个表时,取的是两个表中都存在的数据。(取交集)
select * from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.列=表2.列
或
select * from 表1,表2 where 表1.列=表2.列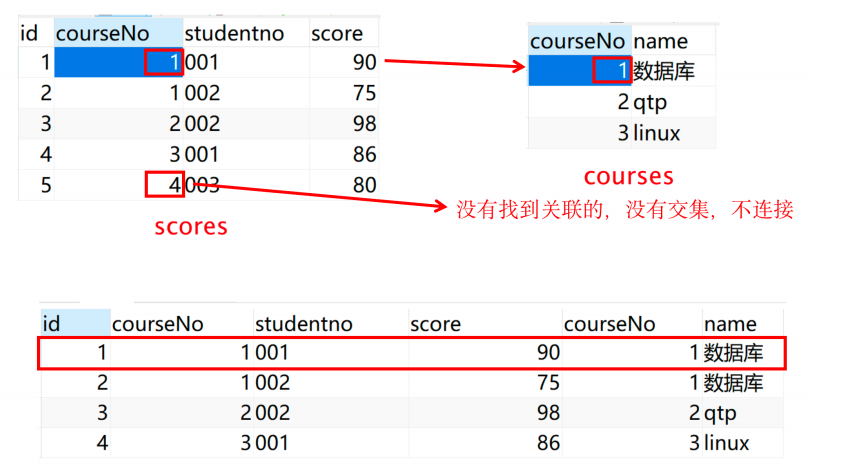
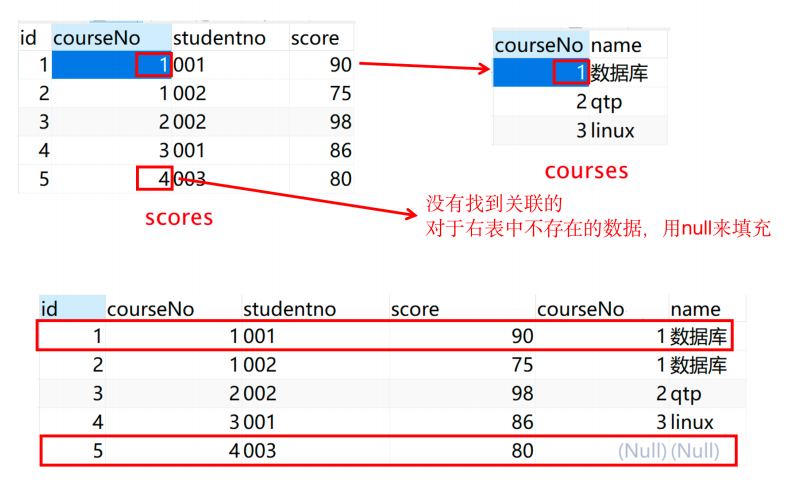
左连接
left join: 连接两个表时,取的是左表中特有的数据,对于右表中不存在的数据,用null来填充。
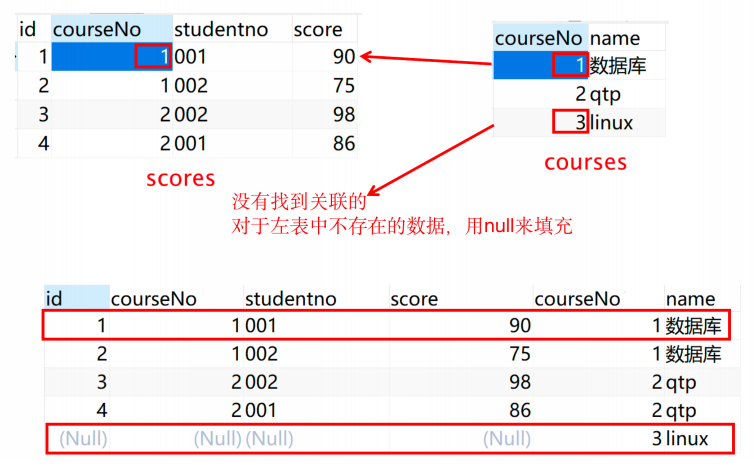
右连接
right join:连接两个表时,取的是右表中特有的数据,对于左表中不存在的数据,用null来填充
七、自关联查询(重点)
自连接的应用场景
省、市、区的信息,一般不会分开放在不同的表里面进行存储,而是放在同一个表当中。
又比如商品分类的,大类和细分类,一般也是放在同一个表中。

自关联实现
要通过自关联进行查询时,当前自关联的表当中一定会存在两个相关联的字段
自关联要用别名,把省市表用别名命名为两个别名,方便查询。如下
select * from 表名 as 别名1 inner join 表名 as 别名2 on 别名1.列=别名2.列例1:查询河南省所有的市
Select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='河南省';
例2:查询郑州市的所有的区
Select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid where a1.atitle='郑州市';
例3:查询河南省的所有的市区
Select * from areas as a1 inner join areas as a2 on a1.aid=a2.pid inner join areas as a3 on a2.aid=a3.pid where a1.atitle='河南省'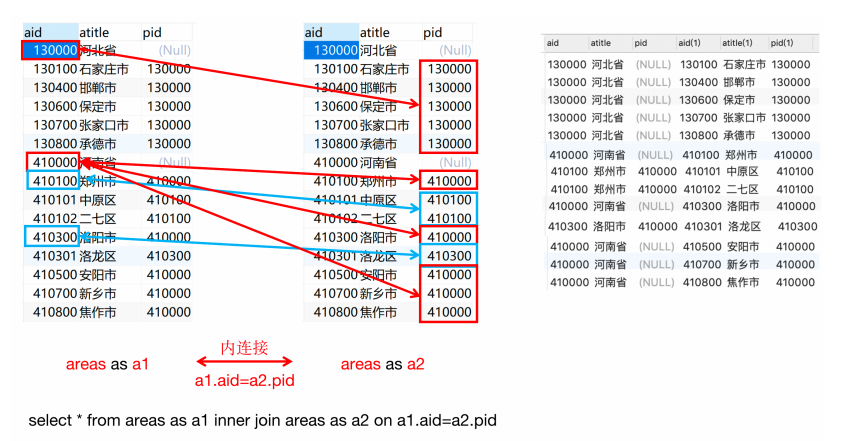
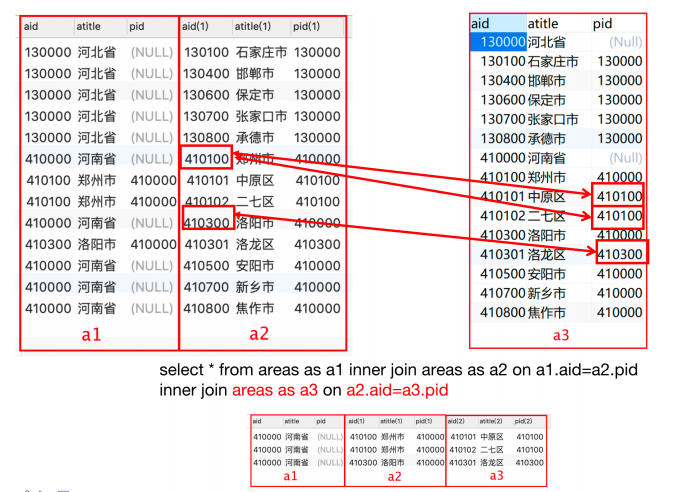
八、子查询
- 将一条SQL查询的语句嵌入在其他的SQL语句中,被嵌入的SQL语句称之为子查询,其他的SQL称之为主查询
- 子查询辅助主查询,要么充当条件,要么充当数据源。
- 子查询是一条完整的、可单独执行的select查询语句。
充当条件
例1:查询王昭君的成绩,要求显示成绩(标量子查询)
select * from scores where studentNo = (select studentNo from students where name = '王昭君')
例2:查询18岁的学生的成绩,要求显示成绩(列子查询)
select * from scores where studentNo in (select studentNo from students where age=18)
例3:查询和王昭君同班、同龄的学生信息(行子查询)
select * from students where (class,age)=(select class,age from students where name='王昭君')充当数据源
例1:查询数据库和系统测试的课程成绩
Select * from scores s inner join (select * from courses where name in ('数据库
','系统测试')) c on s.courseNo = c.courseNo
特定关键字
| 关键字 | 格式 |
| in 范围 | 格式: 主查询 where 条件 in (列子查询) |
| any|some 任意 | 格式: 主查询 where 列 = any(列子查询) |
| all 所有 | 格式: 主查询 where 列 = all(列子查询) |